Online Arbitrage: A Practical Guide to Selling on Amazon
Online Arbitrage: A Practical Guide to Selling on Amazon
Online arbitrage is a business model in which sellers purchase products at lower prices from online retailers and resell them on Amazon for a profit. It allows sellers to leverage existing demand without creating their own products or managing manufacturing processes.
Because the entire process can be handled online, online arbitrage is one of the most accessible ways to start selling on Amazon.
What Is Online Arbitrage?
Online arbitrage is based on price differences between marketplaces. Products may be discounted on websites such as Walmart or Target while maintaining higher selling prices on Amazon. Sellers identify these price gaps and resell the products after accounting for fees and costs.
These differences exist because retailers apply different pricing strategies, promotions, and inventory clearance schedules.
Why Online Arbitrage Is Suitable for Beginners
Online arbitrage is often preferred by beginners due to its relatively low risk and simple structure.
Key advantages include:
- No product manufacturing or branding required
- Lower starting capital compared to wholesale or private label
- Ability to operate fully online
- Immediate access to Amazon’s existing customer base
Many sellers begin with online arbitrage on a small scale and expand gradually as they gain experience.
How Online Arbitrage Works
1. Create an Amazon Seller Account
Sellers register through Amazon Seller Central. A professional seller account is commonly used to access advanced selling features and reports.
2. Use Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
With Fulfillment by Amazon, Amazon handles storage, shipping, customer service, and returns. Products fulfilled through FBA are eligible for Prime shipping, which improves visibility and conversion rates.
3. Research Products
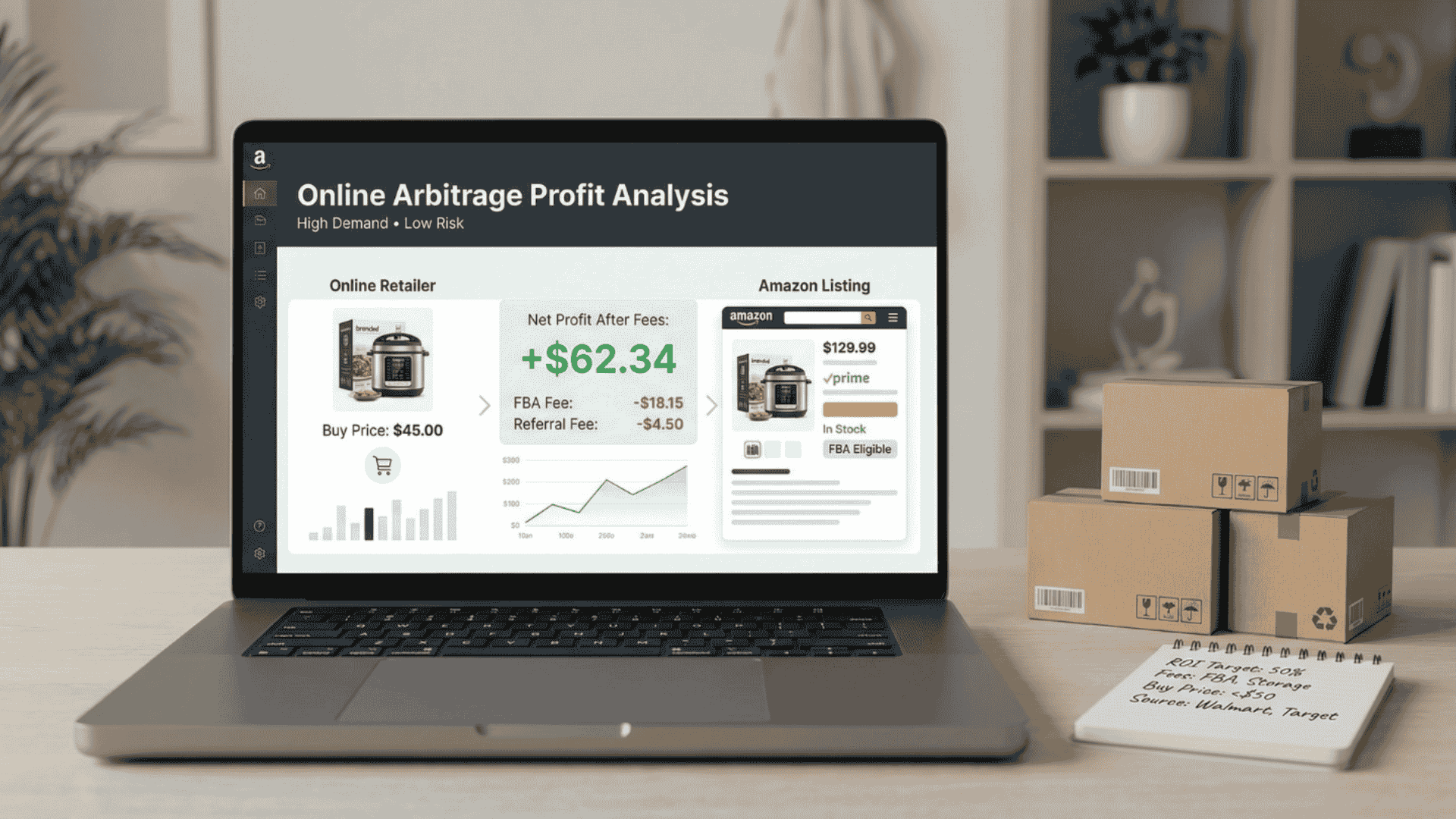
Sellers compare products listed on online retailers such as Walmart or Target with existing Amazon listings. Important factors include demand, competition, Amazon fees, and selling eligibility.
Arbigain supports this step by analyzing products across marketplaces and calculating net profitability after Amazon fees.
4. Purchase and Ship Inventory
Once a product meets profitability criteria, inventory is purchased and shipped to Amazon fulfillment centers. After processing, the product becomes available for sale.
Understanding Profitability in Online Arbitrage
Profitability must be calculated before purchasing any product.
Costs to consider include:
- Product purchase price
- Amazon referral and fulfillment fees
- Shipping to Amazon warehouses
- Storage fees
- Returns and price changes
Profit formula:
Selling Price − (Product Cost + All Fees) = Net Profit
Accurate calculations reduce the risk of unprofitable purchases.
Online Arbitrage vs. Retail Arbitrage
Retail arbitrage involves sourcing products from physical stores, while online arbitrage is done entirely online.
Online arbitrage generally offers:
- Broader product selection
- Easier scalability through online ordering
- Lower time and transportation costs
- Better tracking of orders and invoices
For sellers focused on efficiency and scale, online arbitrage is often the preferred option.
Is Online Arbitrage Still Profitable in 2025?
Online arbitrage remains profitable because pricing inefficiencies continue to exist across online markets. Retailers frequently discount products independently of Amazon pricing.
Long-term profitability depends on:
- Consistent product research
- Clear buying criteria
- Controlled inventory levels
- Reinvestment of profits
Structured analysis tools such as Arbigain help sellers focus on products with realistic profit potential.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes include:
- Ignoring Amazon fees and storage costs
- Purchasing restricted or ineligible products
- Investing too much capital in a single product
- Entering price competition without sufficient margins
- Holding slow-moving inventory for too long
Avoiding these mistakes improves sustainability.
Scaling an Online Arbitrage Business
As experience increases, sellers can scale by building repeatable systems.
Typical scaling steps include:
- Defining consistent sourcing rules
- Expanding into new categories gradually
- Outsourcing preparation and logistics
- Prioritizing inventory turnover over individual margins
Data-driven decision-making becomes increasingly important at scale.
Conclusion
Online arbitrage is a practical and proven way to start selling on Amazon. Sellers who approach it with discipline, accurate calculations, and structured processes can build a stable and scalable business.
With proper analysis and tools such as Arbigain, online arbitrage can grow from a beginner-friendly entry point into a long-term e-commerce operation.
Author: Clara Jensen
